
Overview
The client needed a solution that could provide AI-powered responses based on custom documents uploaded by users. Manual processing of files and integrating them with AI models would be slow and error-prone. The goal was to build a RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) system that:
- Reads and processes uploaded PDF and DOCX files.
- Splits them into manageable chunks for embedding.
- Stores embeddings in a vector database (Qdrant).
- Enables users to query and chat with an AI trained on these documents.
Challenge
Traditional AI models cannot directly interact with user-uploaded files, and large documents are often too big to fit into memory for processing. The challenges were:
- Handling multiple document types (PDF, DOCX) reliably.
- Avoiding duplicate processing of the same files.
- Efficiently splitting documents into embeddings for retrieval.
- Providing real-time, context-aware AI responses to user queries.
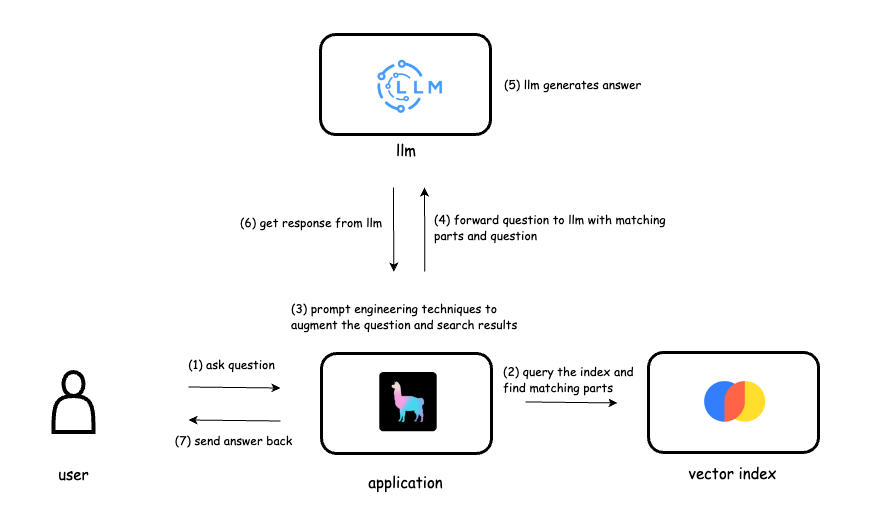
Solution
The solution involved a combination of Python, LangChain, Qdrant, and asynchronous AI APIs. The process had two main parts:
1. Document Ingestion
We created a script that:
- Checks the Qdrant vector database for already ingested files to prevent duplicates.
- Iterates over new files in a specified folder.
- Loads the file using the appropriate loader (
PyPDFLoaderfor PDFs,Docx2txtLoaderfor DOCX). - Splits the document into chunks using
RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter. - Adds the chunks to the Qdrant vector store with metadata for retrieval.
async def add_documents_from_folder(folder_path="../filesInEnglish"):
existing_filenames = set()
next_offset = None
while True:
scroll_result, next_offset = qdrant_client.scroll(
collection_name=COLLECTION_NAME,
limit=1000,
with_payload=True,
offset=next_offset
)
for point in scroll_result:
if "filename" in point.payload:
existing_filenames.add(point.payload["filename"])
if next_offset is None:
break
for filename in os.listdir(folder_path):
if not (filename.endswith(".pdf") or filename.endswith(".docx")):
continue
if filename in existing_filenames:
print(f"⏩ Skipping {filename} (already exists in DB)")
continue
print(f'Processing file: {filename}')
file_path = os.path.join(folder_path, filename)
loader = PyPDFLoader(file_path) if filename.endswith(".pdf") else Docx2txtLoader(file_path)
docs = loader.load()
splitter = RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter(chunk_size=500, chunk_overlap=50)
chunks = splitter.split_documents(docs)
print(f'Number of chunks created: {len(chunks)}')
texts = [chunk.page_content for chunk in chunks]
metadatas = [{"filename": filename, "chunk": i} for i in range(len(chunks))]
vectorstore.add_texts(texts=texts, metadatas=metadatas)
print(f'Done adding {len(chunks)} chunks to Qdrant of {filename}')
sleep(5) # To avoid overwhelming the serverThis Design Ensures
- Users receive responses based on their uploaded content.
- The AI system remains responsive and contextually accurate.
- Easy scalability by adding new documents to the vector store.
Implementation Highlights
- Async document ingestion with deduplication to prevent redundant processing.
- Vector database integration using Qdrant for fast similarity search.
- Chunking strategy ensures even large files are searchable without memory issues.
- Seamless AI query using LangChain messages and async calls.
- File type flexibility with support for both PDF and DOCX formats.
Outcome
- Built a fully functional RAG system capable of handling user-uploaded files in real-time.
- Enabled AI to provide accurate, context-driven responses from custom documents.
- Efficient ingestion and embedding prevented unnecessary reprocessing.
- Scalable design supports growing document libraries without performance degradation.
Conclusion
This project demonstrates the power of combining vector databases, document chunking, and AI APIs to create interactive, intelligent applications. The RAG system allows organizations to empower users with AI that understands their unique content, paving the way for smarter search, chat, and content-driven insights.
Read more
Building a RAG Application for AI-Powered File Interaction
A case study on developing a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) system that allows users to interact with AI trained on uploaded documents.

Automating EC2 & JupyterHub Provisioning: Reducing Deployment Time from Hours to Minutes
A senior-engineer case study on converting a manual AWS provisioning workflow into a fully automated system using AWS SDK, IAM, S3, and EC2 orchestration.
Architecting a Scalable Learning Management Platform with React, Node.js, and AWS
A case study on migrating a monolithic LMS to a modular, microservices-inspired architecture with high scalability, real-time analytics, and multi-role support.