
Building a scalable learning management platform that handles thousands of concurrent learners requires careful architecture, efficient data handling, and reliable infrastructure.
In a previous project, the LMS platform was monolithic, resulting in slow development, scalability issues, and unreliable analytics. The goal was to transform it into a modular, service-oriented architecture using React, Node.js, and AWS services.
Challenge
The monolithic LMS suffered from multiple issues:
- Scalability bottlenecks: Single servers could not handle concurrent users efficiently
- Slow release cycles: Adding new features required changes across the entire codebase
- Analytics inefficiency: Real-time learner progress tracking stressed the database
- Global accessibility: Static content delivery was slow for users far from the server
- Single point of failure: Any downtime affected all users
Manual scaling and infrastructure management could not keep up with the platform's growth. A solution that ensured high availability, reliability, and faster development was essential.
Goals
The engineering objectives were:
- Modular service-oriented architecture to isolate functionalities
- Horizontal scalability with AWS EC2 and Dockerized services
- Real-time analytics without overloading the database
- Secure API authentication with JWT and role-based access
- Efficient static content delivery via AWS S3 and CloudFront
- Improved developer productivity through independent service deployment
Solution
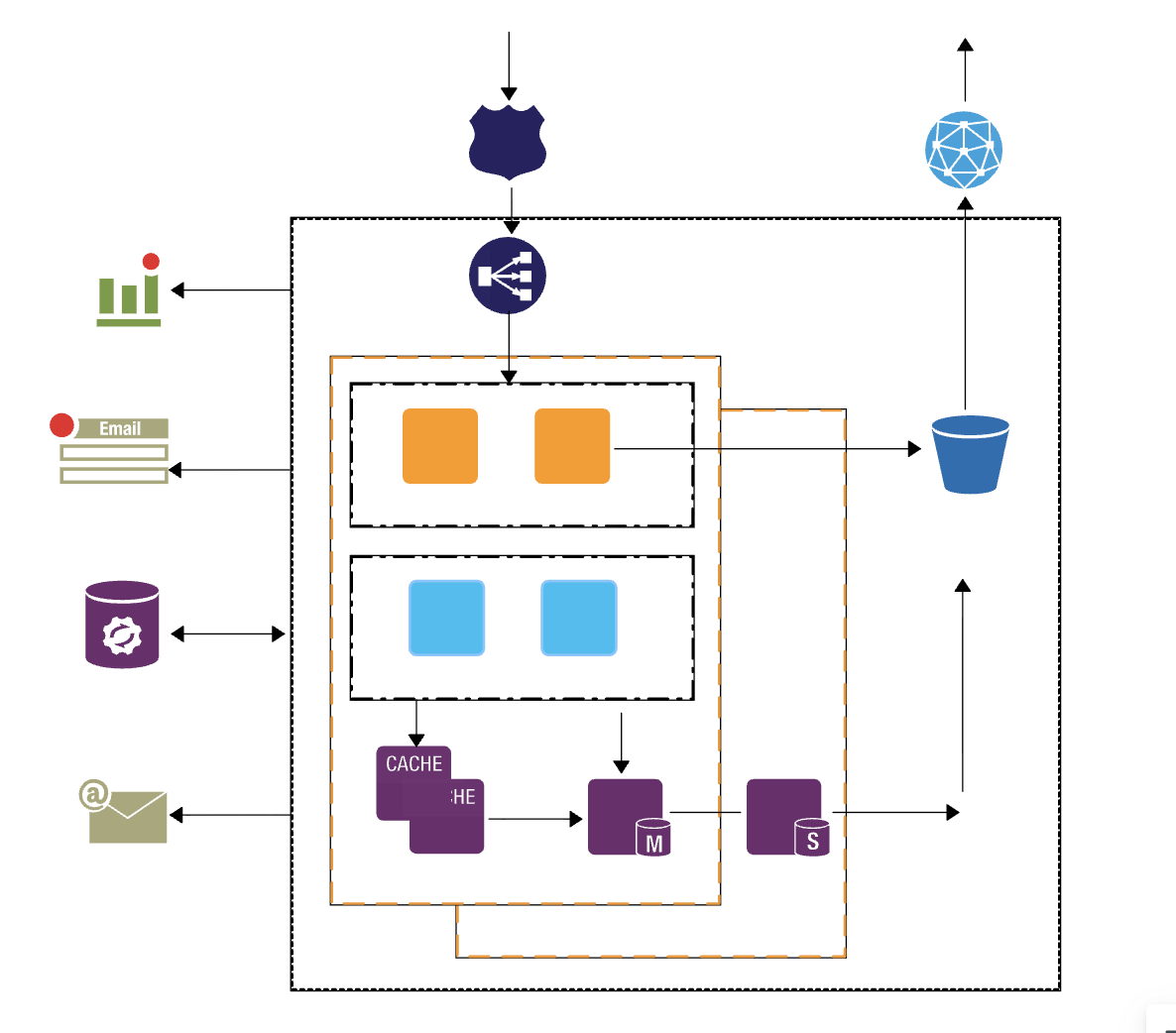
The platform was re-architected as follows:
- Backend: Node.js microservices handling users, courses, analytics, and content
- Database: MongoDB for course and user data, using normalized and denormalized structures
- Caching Layer: Redis for frequently accessed data and session management
- Authentication: JWT with refresh tokens and role-based middleware
- Static Assets: S3 for storage, CloudFront for global delivery
- Deployment: Docker containers orchestrated behind Nginx reverse proxy
- Monitoring: AWS CloudWatch for logs and performance metrics
This modular approach allowed each service to scale independently and reduced interdependencies.
Implementation Highlights
// Example: Dockerized microservices for modular LMS backend
// 1. User Service
app.post('/users', createUser);
app.get('/users/:id/progress', getUserProgress);
// 2. Course Service
app.post('/courses', createCourse);
app.get('/courses/:id/content', getCourseContent);
// 3. Analytics Service
app.get('/analytics/user/:id', getUserAnalytics);
app.get('/analytics/course/:id', getCourseAnalytics);
// 4. Caching Layer
redis.set(`user:${userId}:progress`, JSON.stringify(progress));
redis.get(`user:${userId}:progress`);
// 5. Static Content Delivery
// Assets stored in S3 and delivered via CloudFront
// 6. Deployment
// Docker containers for each service, orchestrated with Nginx reverse proxyOutcome
The new architecture produced tangible results:
- Supported 5,000+ concurrent users with consistent performance
- API latency reduced to sub-200ms
- Infrastructure costs reduced by 30% through caching and auto-scaling
- Faster development cycles due to modular services
- Reliable, real-time progress tracking for learners
- Global content delivery ensured low latency for users worldwide
Conclusion
Migrating the LMS to a microservices-inspired modular architecture transformed the platform from a monolithic, constrained system into a scalable, maintainable, and high-performing solution.
The new design allows teams to deploy features independently, monitor system performance efficiently, and support an increasing number of learners without additional operational burden. By leveraging Docker, AWS services, and caching strategies, the platform became future-proof, fast, and reliable, setting a strong foundation for ongoing growth and innovation.
Read more
Architecting a Scalable Learning Management Platform with React, Node.js, and AWS
A case study on migrating a monolithic LMS to a modular, microservices-inspired architecture with high scalability, real-time analytics, and multi-role support.

Automating EC2 & JupyterHub Provisioning: Reducing Deployment Time from Hours to Minutes
A senior-engineer case study on converting a manual AWS provisioning workflow into a fully automated system using AWS SDK, IAM, S3, and EC2 orchestration.
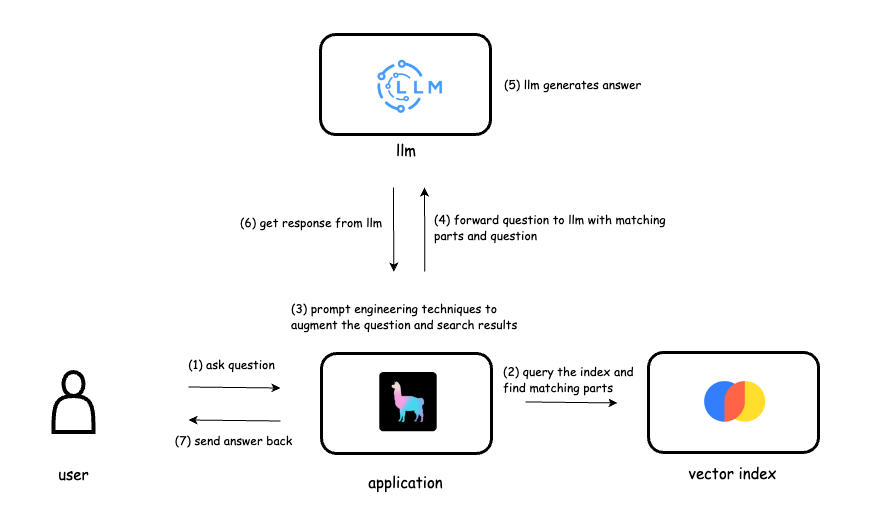
Building a RAG Application for AI-Powered File Interaction
A case study on developing a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) system that allows users to interact with AI trained on uploaded documents.